Structural Bioinformatics
Baldo Oliva
Group website
Research Outline
Macromolecular interactions play a relevant role among the different functions of a cell. Identifying the protein-protein interaction network of a given organism (interactome) is useful to shed light on the key molecular mechanisms within a biological system. We interrogate protein structure to unveil its function, generate the network of interactions and relate genes/proteins with diseases by exploiting the topology of the network. Similarly, the regulatory network implies the formation of a large macromolecular complex of transcription in which proteins interact with DNA. We also interrogate the structure of these complexes to relate other types of mutations affecting the final network.
Research Lines
isPBM (in silico protein binding micro-arrays): Structural modelling of the binding between transcription-factors and DNA with biomedical applications in networks and systems medicine
We use the structures of transcription-factor (TF) complexes with DNA to calculate family-specific statistic potentials for the amino-acid-nucleotide interactions and characterize the specificity of the interactions between TFs and their DNA motifs. We computationally create Position-Weight-Matrices (PWMs) of TFs based on modelling structures and study: 1) the prediction of DNA binding motifs; 2) the change of specificity caused by mutations; and 3) produce a protein-engineering of a TF highly specific for a DNA motif. We analyse how the changes of specificity of TF-DNA interactions caused by mutations affect the rewiring of the protein-interaction network. Our goal is to understand the mechanisms of recognition and interaction of TFs with their corresponding DNA binding site, focused on biomedical applications in networks and systems medicine.
Team during 2019-20
PhD students: Joaquim Aguirre-Plans, Alberto Meseguer
Technicians: Ruben Molina-Fernandez
Selected publications
-
Sharma P., Lioutas A., Fernandez-Fuentes N., Quilez J., Carbonell-Caballero J., Wright RHG, Di Vona C, Le Dily F., Schüller R., Eick R., Oliva B., Beato M. (2019) Arginine citrullination at the C-terminal domain controls RNA polymerase II transcription. Molecular cell 73(1):84-96 e7
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2018.10.016
Blasco-Moreno B., de Campos-Mata L. , Böttcher R. , García-Martínez J., Jungfleisch J., Nedialkova DD, Chattopadhyay S, Gas ME, Oliva B, Pérez-Ortín JE, Leidel SA, Choder M, Díez J (2019) The exonuclease Xrn1 activates transcription and translation of mRNAs encoding membrane proteins Nature communications 10 (1): 1-15. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09199-6
Aguirre-Plans J, Piñero J, Sanz F, Furlong LI, Fernandez-Fuentes N, Oliva B, Guney E (2019) GUILDify v2. 0: a tool to identify molecular networks underlying human diseases, their comorbidities and their druggable targets. Journal of molecular biology 431 (13): 2477-2484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2019.02.027
Meseguer A, Årman F, Fornes O, Molina-Fernández R, Bonet J, Fernandez-Fuentes N, Oliva B. (2020) On the prediction of DNA-binding preferences of C2H2-ZF domains using structural models: application on human CTCF. NAR Genomics and Bioinformatics 2 (3), lqaa046. https://doi.org/10.1093/nargab/lqaa046
Meseguer A, Dominguez L, Bota PM, Aguirre‐Plans J, Bonet J, Fernandez‐Fuentes N, Oliva B. (2020) Using collections of structural models to predict changes of binding affinity caused by mutations in protein‐protein interactions. Protein Science 29 (10), 2112-2130. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.3930
Other relevant information
Patent: B. Oliva, D. Andreu, A. Sierra & N Fernandez-Fuentes. Peptides for the treatment of Cancer. Institution: UPF, Fundació Universitaria Balmes (UVic). N/Ref Europe EP20382901-5-1112
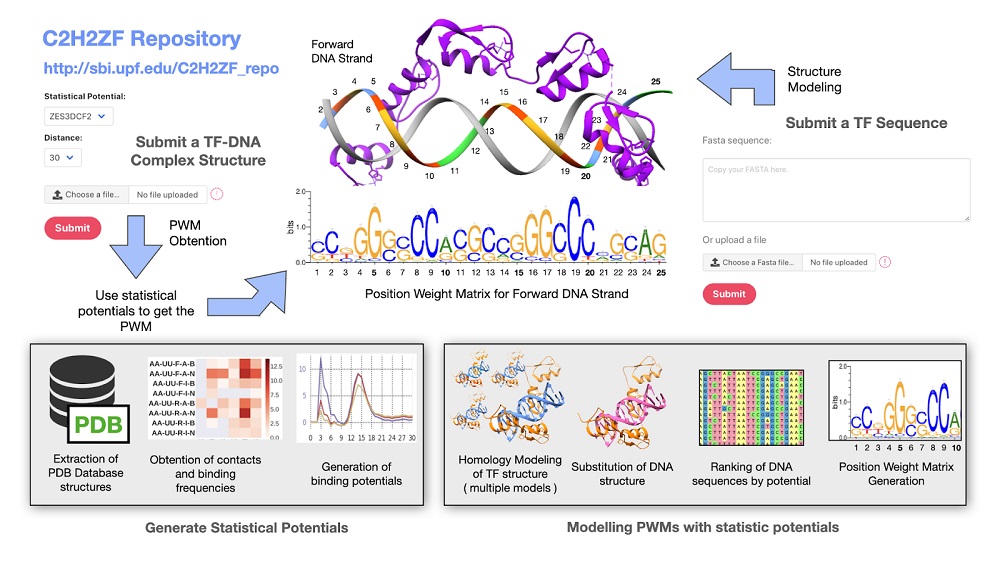
Scheme of the method to model and predict the Position Weight Matrix (PWM) of Zinc-fingers. We display a partial model of the structure of human CTCF (C2H2-ZFs domains 6 to 11) binding a DNA molecule and its predicted PWM. The forward strand, oriented to calculate the PWM, is colored in the ribbon-plate. At the bottom of the figure, we show the steps to extract contact frequencies between amino acids and nucleotides to construct the statistical potentials and its application to predicting a PWM by ranking the best-scored DNA.
