Human Natural Killer Cell Biology
Miguel López-Botet

Group website
Research Outline
-
The group gathers researchers from UPF and IMIM, under the coordination of Prof. Miguel López-Botet. The team has broad experience in the biology of human Natural Killer (NK) cells, which are involved in the immune response to pathogens and tumors. NK cells may eliminate infected and transformed cells while promoting the development of specific adaptive immunity.
-
Most relevant past contributions include the characterization of CD94/NKG2 and ILT2 (LIR-1 or LILRB1) receptors and the original identification of the adaptive NK cell response to human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection.
Research Lines
1) Characterization of NK cell receptors and their involvement in the response to human cytomegalovirus (HCMV). Miguel López-Botet (UPF/IMIM)
-Unravel the mechanisms which drive the adaptive differentiation and expansion of NK cells in response to the viral infection.
-Study the role of adaptive NK cells in the control of HCMV infection in immunosuppressed kidney transplant recipients.
(in collaboration with the Nephrology and Immunology Depts. at Hospital del Mar)
2) Natural Killer cells in cancer immunotherapy. Aura Muntasell (IMIM)
- Identification of targetable checkpoints enhancing NK cell recruitment, persistence and function in the tumor microenvironment.
- Study of NK cells as biomarkers of response/resistance to treatment in breast and colorectal cancer.
- Development of protocols for optimizing NK cell-based cancer therapy and patient monitorization.
(in collaboration with the Medical Oncology, Pathology and Surgery Depts. at Hospital del Mar)
Team during 2019-20
PhD students: Michelle Ataya, Mireia Altadill, Anna Rea, Mariona Cabo
Postdocs: Elisenda Alari
Technicians: Gemma Heredia, Sara Santana, Araceli Cuélliga
Senior scientist: Aura Muntasell
Selected publications
-
Ataya M, Redondo-Pachón D, Llinàs-Mallol L, Yélamos J, Heredia G, Pérez-Sáez MJ, Vila J, Costa-García M, Raïch-Regué D, Vilches C, Pascual J, Crespo M, López-Botet M. (2020) Pretransplant adaptive NKG2C+ NK cells protect against cytomegalovirus infection in kidney transplant recipients. Am J Transplant. Mar;20(3):663-676. doi: 10.1111/ajt.15658. Epub 2019 Nov 19. PMID: 31612635.
-
Muntasell A, Servitja S, Cabo M, Bermejo B, Pérez-Buira S, Rojo F, Costa-García M, Arpí O, Moraru M, Serrano L, Tusquets I, Martínez MT, Heredia G, Vera A, Martínez-García M, Soria L, Comerma L, Santana-Hernández S, Eroles P, Rovira A, Vilches C, Lluch A, Albanell J, López-Botet M. (2019) High Numbers of Circulating CD57<sup>+</sup> NK Cells Associate with Resistance to HER2-Specific Therapeutic Antibodies in HER2<sup>+</sup> Primary Breast Cancer. Cancer Immunol Res. Aug;7(8):1280-1292. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-18-0896. Epub 2019 Jun 12. PMID: 31189644.
-
Costa-García M, Ataya M, Moraru M, Vilches C, López-Botet M, Muntasell A. (2019) Human Cytomegalovirus Antigen Presentation by HLA-DR+ NKG2C+ Adaptive NK Cells Specifically Activates Polyfunctional Effector Memory CD4+ T Lymphocytes. Front Immunol. Apr 3;10:687. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00687. PMID: 3100128.
-
Moreira A, Alari-Pahissa E, Munteis E, Vera A, Zabalza A, Llop M, Villarrubia N, Costa-García M, Álvarez-Lafuente R, Villar LM, López-Botet M, Martínez-Rodríguez JE. (2019) Adaptive Features of Natural Killer Cells in Multiple Sclerosis. Front Immunol. Oct 15;10:2403. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02403. PMID: 31681293.
-
Muntasell A, Rojo F, Servitja S, Rubio-Perez C, Cabo M, Tamborero D, Costa-García M, Martínez-Garcia M, Menéndez S, Vazquez I, Lluch A, Gonzalez-Perez A, Rovira A, López-Botet M, Albanell J. NK Cell Infiltrates and HLA Class I Expression in Primary HER2<sup>+</sup> Breast Cancer Predict and Uncouple Pathological Response and Disease-free Survival. Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Mar 1;25(5):1535-1545. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-2365. Epub 2018 Dec 6. PMID:30523021.
Other relevant information
License agreement HP-DM1 monoclonal antibody Biolegend
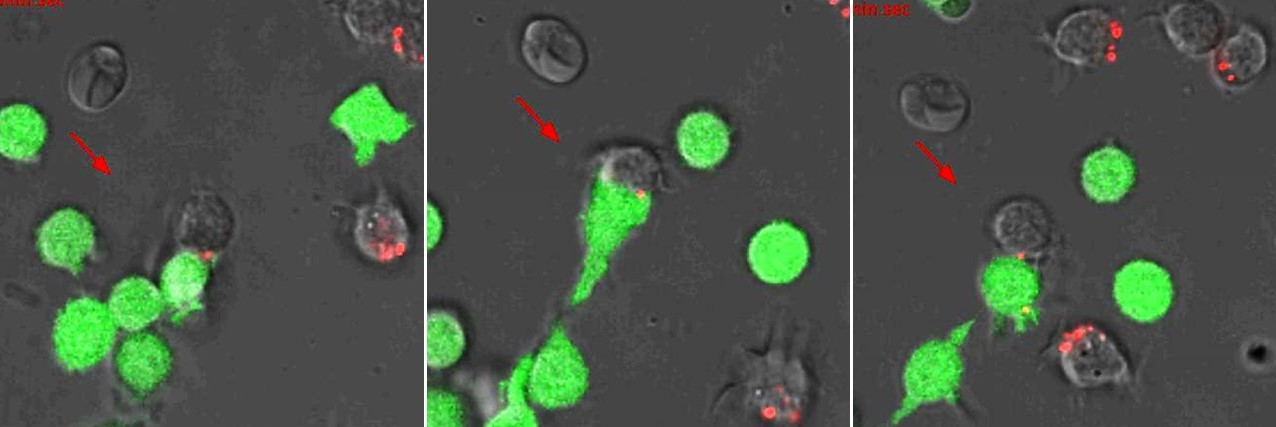
NK cells (green) eliminate Epstein-Barr virus (red) bound to B cells (grey) through a specific antibody-mediated uptake (Alari-Pahissa et al.)
