The tones and intonation of second languages are better learned with gestures
The tones and intonation of second languages are better learned with gestures
According to two articles on the learning of Spanish and Mandarin Chinese, respectively, carried out by the Prosodic Studies Group led by Pilar Prieto, ICREA researcher at the Department of Translation and Language Sciences, published with members her team in the journal Studies in Second Language Acquisition.

Recent studies on the learning of the prosody of a second language (accent, tone and intonation, rhythm, speed) have suggested that gestures of tonality can help in the learning of lexical tones. One of the research areas of the Prosodic Studies Group (GrEP), led by Pilar Prieto, ICREA researcher at the Department of Translation and Language Sciences (DTCL) at UPF, deals with how intonation and gestural language are involved in the learning of a second language.
To find out if the use of gestures can help to learn intonation, especially for speakers of a tonal language, two recent papers by this group, published in the journal Studies in Second Language Acquisition, have investigated how gestures of tonality can bring benefits to second-language learning.
Mandarin Chinese-speaking students of the University of Xi’an (China) were posed with learning three basic level patterns of intonation in Spanish
In an initial study, the experimental design involved Mandarin Chinese-speaking students of the University of Xi’an (China), who were posed with learning three basic level patterns of intonation in Spanish. Half of the participants (control group) received intonation training without using gestures of tonality, the other half received the same training but with gestures of tonality, using the hands to mimic the intonation (experimental group). In addition, the researchers took into account and measured the musical skills of the participants (melody, tonality).
The results highlighted that the experimental group improved significantly in the learning of Spanish intonation and, although those with strong musical skills had advantages, participants with weaker musical skills benefited to a greater extent from the observation of gestures of tonality.
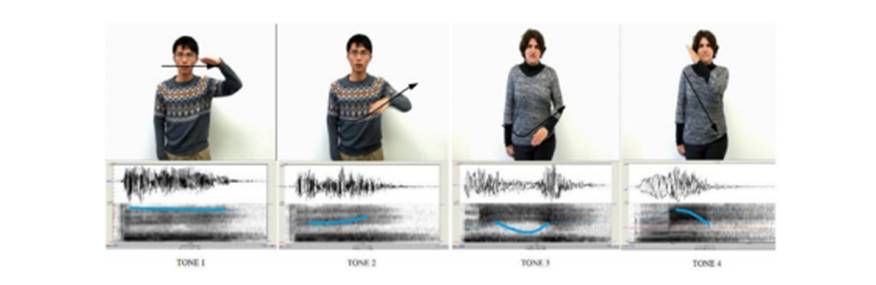 In the second study, 106 participants without prior knowledge of Mandarin Chinese were asked to perform a task of observation (experiment 1) and of production (experiment 2) of Chinese tones and words using gestures of tonality in a session of identifying tones and of learning words.
In the second study, 106 participants without prior knowledge of Mandarin Chinese were asked to perform a task of observation (experiment 1) and of production (experiment 2) of Chinese tones and words using gestures of tonality in a session of identifying tones and of learning words.
Both the tasks of perception and of production with gestures of tonality are beneficial learning strategies for the initial stages of the acquisition of tones for learners of Chinese as a second language
The results showed the positive effect of a training session with the observation of gestures of tonality in comparison with a training session without (Experiment 1) and the benefits of producing gestures in comparison with only observing them and repeating the words out loud (Experiment 2).
To compare the results of the two experiments, no significant difference was observed between the observation of gestures of tonality in silence and the production of speech accompanied by gestures of tonality, in the ease of identifying lexical tone and the learning of words. Therefore, both the perceptual tasks and those of production with gestures of tonality can be considered as beneficial learning strategies for the initial stages of the acquisition of tones for learners of Chinese as a second language.
Related works:
Chenjie Yuan, Santiago González-Fuente, Florence Baills, Pilar Prieto (2018), “Observing pitch gestures favors the learning of Spanish intonation by Mandarin speakers", Studies in Second Language Acquisition, published in advanced online, 2 january, pp 1-28.
Florence Baills, Nerea Suárez-González, Santiago González-Fuente, Pilar Prieto (2018), "Observing and Producing Pitch Gestures Facilitates the Learning of Mandarin Chinese Tones and Words", Studies in Second Language Acquisition, pp. 1-26, DOI:10.1017/S0272263118000074
