A medical image segmentation method achieves the best performance at Challenge NeoBrainS12
Developed by researchers of the Simbiosys Research Group, the authors described it in a paper presented at the 7th International Workshop on Machine Learning in Medical Imaging, held on 17 October in Athens (Greece).
Brain tissues and structures are studied on the basis of medical imaging and are then processed and interpreted through segmentation methods with the aim of supporting image-based diagnosis. Today, the two most commonly used methodologies in the segmentation of structures are based on the modelling of the intensities of the tissues and multi-atlas fusion.
Computing plays a fundamental role in the development of new techniques for the acquisition and quantitative analysis of medical images obtained by means of intracranial magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Although the experts in neuroimaging can perform this task manually, it is a slow process. Hence, the development of automatic methods to precisely characterize the main brain structures is crucial to help with diagnosis. The automatic method is quick, objective, and achieves reproducible methods for a large amount of data.
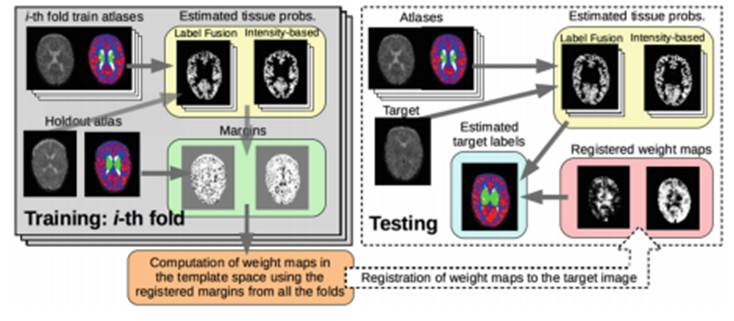
Researchers with Simbiosys (Simulation, Imaging and Modelling for Biomedical Systems), the research group of the Department of Information and Communication Technologies (DTIC) at UPF, have developed a new method of segmentation that combines complementary characteristics of the two habitually used methods, cited above, and obtain better results.
Gerard Sanroma, Oualid M. Benkarim, and Gemma Piella, researchers of the Simbiosys research group, together with Miguel Ángel González Ballester, head of the Group and ICREA research professor at the DTIC, explain the details of this new method in a paper they presented at the 7th International Workshop on Machine Learning in Medical Imaging, held on 17 October in Athens (Greece).
Simbiosys participates in Challenge NeoBrain12
The volume of neonatal brain tissue is considered a good indicator of the efficiency of neurological development in the long term. Quantifying the volume of brain tissue is carried out using image segmentation methods. One practical application of the algorithm created by Simbiosys lies in the participation of the Group at Challenge NeoBrainS12 event. As Sanroma explains: "our image segmentation method in neonatal brains is surpassing the rest of methods presented at the Challenge NeoBrainS12".
Coordinated from the Netherlands, the goal of NeoBrainS12 is to compare the performance of automatic algorithm quantification methods applied to images of neonatal brains following certain protocols. At NeoBrain12, different working groups put forward their algorithms which are compared with the same reference pattern in order to identify the best efficiency. Since 2013, the Simbiosys group has taken part in this challenge and the results suggest that the segmentation method of Sanroma et al., in many of the categories studied for the challenge, is achieving first place, with improvements of up to 10% in performance.
Reference work:
Gerard Sanroma, Oualid M. Benkarim, Gemma Piella, Miguel Ángel González Ballester (2016), “Building an Ensemble of Complementary Segmentation Methods by Exploiting Probabilistic Estimates”, pàgs. 27-25, a: L. Wang et al. (Eds): MLMI 2016, LNCS 10019, Springer International Publishing. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-47157-0_4
